Abstands- und Winkelbestimmungen: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus RSG-Wiki
| Zeile 45: | Zeile 45: | ||
k + (7+k) + (-1+k) + 12 = 0 --> k = -6 und L(-6;1;-7)<br> | k + (7+k) + (-1+k) + 12 = 0 --> k = -6 und L(-6;1;-7)<br> | ||
<math>g^*: \vec{x}=\left( \begin{array}{c} -6 \\\ 1 \\\ -7 \end{array}\right) + r \left( \begin{array}{c} -5 \\\ 6 \\\ -1 \end{array}\right)</math> | <math>g^*: \vec{x}=\left( \begin{array}{c} -6 \\\ 1 \\\ -7 \end{array}\right) + r \left( \begin{array}{c} -5 \\\ 6 \\\ -1 \end{array}\right)</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | S. 154/4 | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Lösung versteckt| Die Ebene E hat HNF <math> \frac{16x_1+ 8x_2 + 2x_3}{18}=0</math> . | ||
| + | Für diese Gleichung hat man also einen Normaleneinheitsvektor <math>\vec{n^o}= \frac{1}{18} \left( \begin{array}{c} 16 \\\ 8 \\\ 2 \end{array}\right) = \frac{1}{9} \left( \begin{array}{c} 8 \\\ 4 \\\ 1 \end{array}\right) </math> . <br> | ||
| + | Zu einer zu E parallelen Ebene im Abstand 9 kommt man, wenn man neun mal diesen Normaleneinheitsvektor <math>\vec{n^o}</math> oder <math>-\vec{n^o}</math> aneinandersetzt. | ||
}} | }} | ||
Version vom 24. März 2020, 19:12 Uhr
Dieses Thema ist im Buch auf S. 151 ausführlich beschrieben. Lesen Sie bitte diese Seite aufmerksam.
Die Hessesche Normalenform (HNF)
Aufgaben
S. 153/1
S. 153/2
S. 154/4
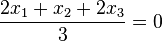 .
. 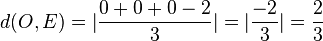 .
.  nimmt man hiervon den Betrag.
nimmt man hiervon den Betrag.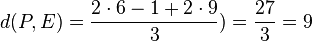
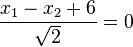 .
. 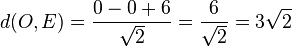 .
. 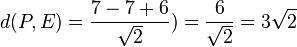 .
.
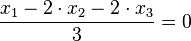 .
. 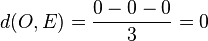 . Der Ursprung liegt in der Ebene E.
. Der Ursprung liegt in der Ebene E. 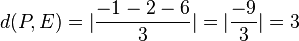 .
.
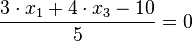 .
. 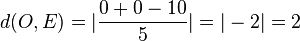 .
. 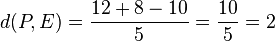 .
.
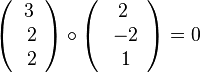 steht der Richtungsvektor
steht der Richtungsvektor  der Geraden g senkrecht zum Normalenvektor
der Geraden g senkrecht zum Normalenvektor 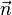 der Ebene E.
der Ebene E. 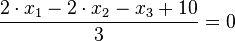 .
Für den Stützpunkt A(7;-13;-4) der Gerade g berechnet man
.
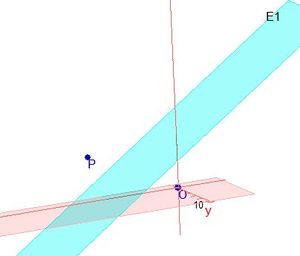
Für den Stützpunkt A(7;-13;-4) der Gerade g berechnet man 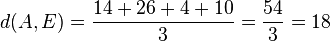 , also liegt A nicht in E und g ist echt parallel zu E. Das g echt parallel zu E ist, hat g auch den Abstand 18 zur Ebene E.
, also liegt A nicht in E und g ist echt parallel zu E. Das g echt parallel zu E ist, hat g auch den Abstand 18 zur Ebene E. 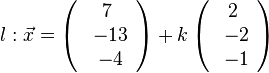 auf E, dann erhält man den Lotfusspunkt L durch 2(7+2k)-2(-13-2k)-(-4-k)+10=0 und k = -6 und L(-5;-1;2). Damit hat man für g* den Stützpunkt. Ihr Richtungsvektor ist derselbe wie bei g, da er "in E liegt" (ist komplanar zu den Richtungsvektoren von E). Die senkrechte Projektion von g in die Ebene E ist dann
auf E, dann erhält man den Lotfusspunkt L durch 2(7+2k)-2(-13-2k)-(-4-k)+10=0 und k = -6 und L(-5;-1;2). Damit hat man für g* den Stützpunkt. Ihr Richtungsvektor ist derselbe wie bei g, da er "in E liegt" (ist komplanar zu den Richtungsvektoren von E). Die senkrechte Projektion von g in die Ebene E ist dann 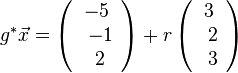 .
.
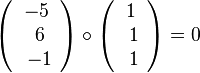 .
.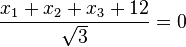 .
.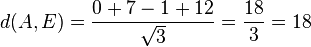
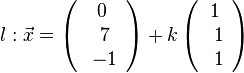
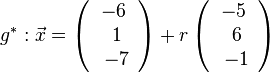
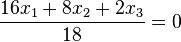 .
.
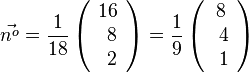 .
. 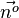 oder
oder 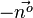 aneinandersetzt.
aneinandersetzt.

