Umkehrfunktion Monotonie
Startseite - Wertetabelle - Graph - Term - Beispiele - Definitions- und Wertemenge - Monotoniekriterium
30px Merke
Eine Funktion Eine Funktion |
Dies heißt, dass bei streng monoton zunehmend mit wachsenden x-Werten auch die y-Werte größer werden. Der Graph geht "bergauf".
Streng monoton abnehmend bedeutet, dass mit wachsenden x-Werten die y-Werte kleiner werden. Der Graph geht "bergab".
30px Aufgabe
|
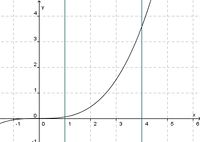 (streng monoton steigend) (!streng monoton fallend) (!weder noch)
(streng monoton steigend) (!streng monoton fallend) (!weder noch)
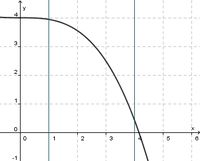 (!streng monoton steigend) (streng monoton fallend) (!weder noch)
(!streng monoton steigend) (streng monoton fallend) (!weder noch)
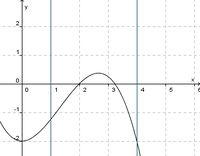 (!streng monoton steigend) (!streng monoton fallend) (weder noch)
(!streng monoton steigend) (!streng monoton fallend) (weder noch)
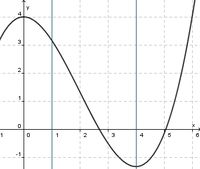 (!streng monoton steigend) (streng monoton fallend) (!weder noch)
(!streng monoton steigend) (streng monoton fallend) (!weder noch)
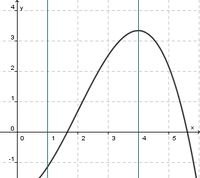 (streng monoton steigend) (!streng monoton fallend) (!weder noch)
(streng monoton steigend) (!streng monoton fallend) (!weder noch)
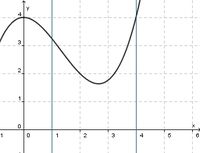 (!streng monoton steigend) (!streng monoton fallend) (weder noch)
(!streng monoton steigend) (!streng monoton fallend) (weder noch)
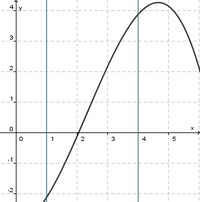 (streng monoton steigend) (!streng monoton fallend) (!weder noch)
(streng monoton steigend) (!streng monoton fallend) (!weder noch)
30px Merke
Ist eine Funktion |
30px Aufgabe
Wo ist die Quadratfunktion Gib jeweils die Umkehrfunktion an. |
Die Quadratfunktion ist im Intervall ![]-\infty;0]](/images/math/6/7/8/6784e26006f1ff6da806742141c799e4.png) streng monoton abnehmend und im Intervall
streng monoton abnehmend und im Intervall 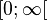 streng monoton zunehmend.
streng monoton zunehmend.
Somit ist der linke Ast ![x \in ]-\infty;0]](/images/math/3/1/7/317c876687f83055d671c49ca798cdf9.png) umkehrbar
umkehrbar
und der rechte Ast 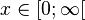 ist ebenso umkehrbar.
ist ebenso umkehrbar.
Für den linken Ast ist 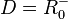 und
und 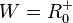 .
.
Umkehrfunktion 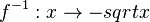 mit
mit 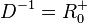 und
und 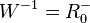 .
.
Für den rechten Ast ist 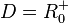 und
und 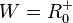
Umkehrfunktion 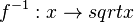 mit
mit 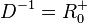 und
und 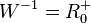 .
.
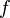 heißt streng monoton zunehmend im Intervall [a;b], wenn für alle
heißt streng monoton zunehmend im Intervall [a;b], wenn für alle ![x_1,x_2 \in [a;b]](/images/math/4/8/9/489a4ad3c2410297428c10a130e7cc95.png) gilt:
gilt: 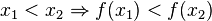
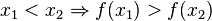
![[a;b]](/images/math/9/4/a/94acf62f087ab3268b2b3fa5a8a7a79c.png) streng monoton, dann ist sie in dem Intervall umkehrbar.
streng monoton, dann ist sie in dem Intervall umkehrbar.
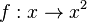 mit
mit 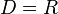 umkehrbar?
umkehrbar?

